Which of the Following Structures Consists Mainly of White Matter
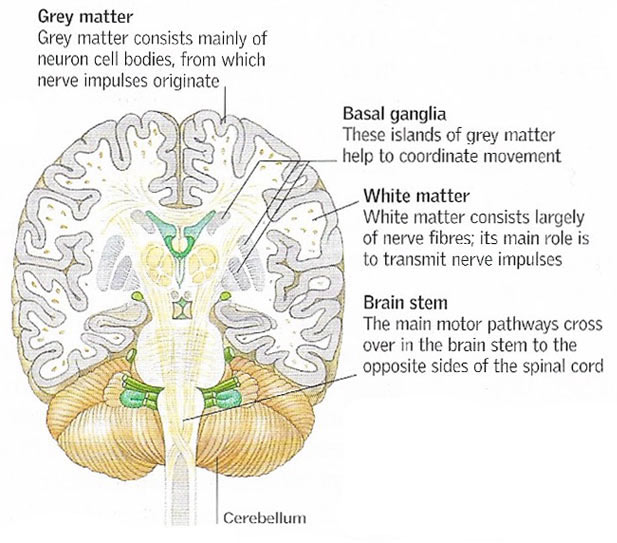
White matter lesions WML are commonly observed on MRI scans in older adults and are thought to occur in the context of cardiovascular disease These age-associated WML have been affiliated with cognitive decline including dementia and also depression and impaired mobility 24Given the diverse nature of these neurological consequences of WML we. While grey matter is primarily associated with processing and cognition white matter modulates the distribution of action potentials acting as a relay and coordinating communication between.

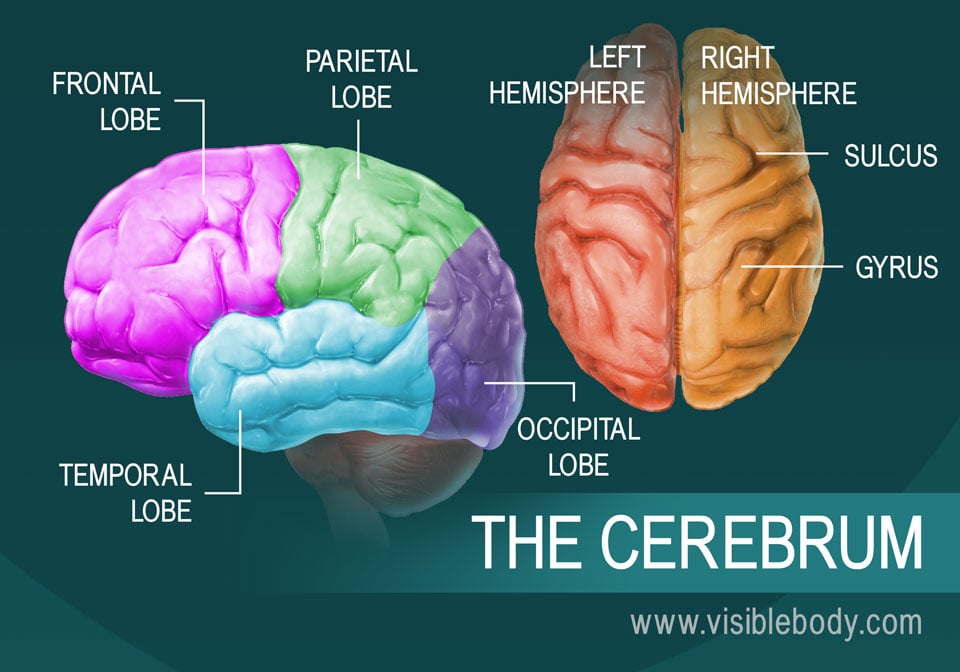
The Cerebrum Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
The axons of white matter transmit signals from various grey matter areas the locations of nerve cell bodies of the cerebrum to each other and carry nerve impulses between neurons.


The Cerebrum Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
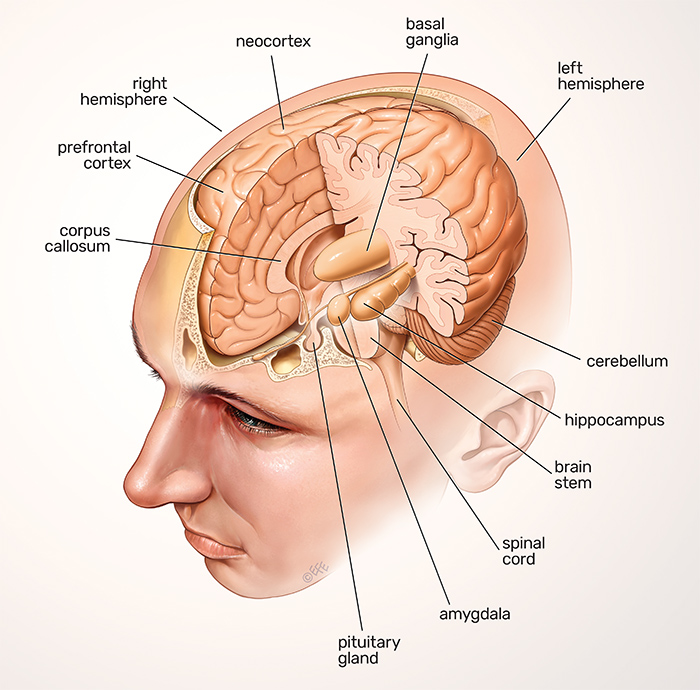
Central Nervous System Brain And Spinal Cord Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland
Thalamic Nuclei Connections Functions And Anatomy Kenhub

All These Images Explain Why Grey Matter And White Matter Are Important There S Also Some Facts And Explanatio White Matter Human Anatomy And Physiology Brain

The Cerebrum Boundless Anatomy And Physiology

Gray Matter Vs White Matter Technology Networks

Grey Matter In The Brain Simply Psychology

Gray And White Matter Structure Functions Location Facts Difference

Gray And White Matter Structure Functions Location Facts Difference

The Cerebrum Boundless Anatomy And Physiology

Gray And White Matter Structure Functions Location Facts Difference

Duke Neurosciences Lab 5 Forebrain Sectional Anatomy

Myelencephalon An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Cerebrum Boundless Anatomy And Physiology

Anatomy Of The White Matter Tracts Osmosis

Gray And White Matter Structure Functions Location Facts Difference
Comments
Post a Comment